Abstract
Introduction. Pediatric stroke is among the leading causes of mortality in children and is associated with significant sequelae in up to 50% of cases, according to published studies. Early acute treatment with tissue plasminogen activator or mechanical thrombectomy improves outcomes in selected cases, reducing the likelihood of neurological sequelae.
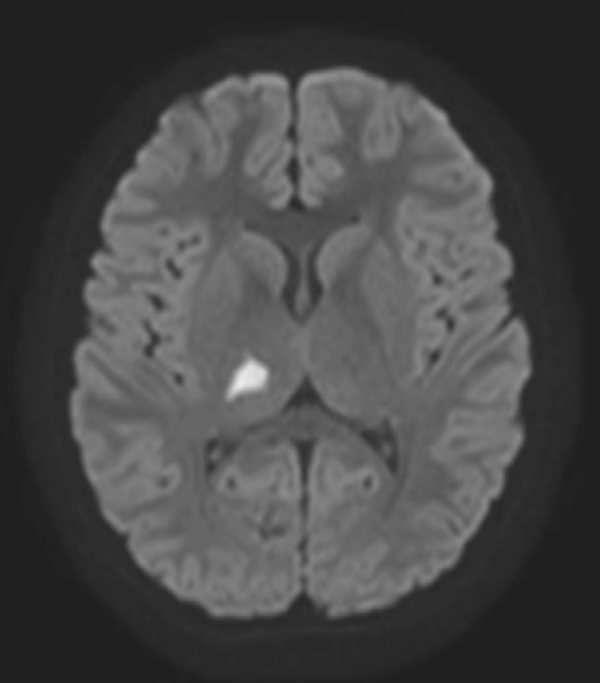
Clinical case: We present the case of an 8-year-old boy who presented with acute-onset oppressive headache, left-sided hemiparesis, ipsilateral sensory deficits, and visual impairment. Suspecting a stroke, an urgent CT angiography of the brain and neck was performed, yielding normal findings. Subsequent MR angiography revealed findings consistent with an acute right thalamic infarction. Etiological workup identified positive SARSCoV-2 serology with elevated anti-spike antibody titers. Intravenous corticosteroid therapy was initiated at a dose of 30 mg/kg.
Conclusions: Early clinical recognition of pediatric stroke is critical for timely and appropriate treatment. The implementation of pediatric stroke protocols can enhance diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic outcomes.
References
Fullerton HJ, Wu YW, Zhao S, Johnston SC. Risk of stroke in children: a population-based study. Lancet Neurol. 2007; 6(6): 481-6.
Mallick AA, Ganesan V, Kirkham FJ, et al. Childhood arterial ischaemic stroke incidence, presenting features, and risk fac- tors: a prospective population-based study. Lancet Neurol. 2014; 13(1): 35-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70290-4
De Castro de Castro P, Simón de las Heras R. Ictus pediátrico. Protoc Diagn Ter Pediatr. 2022; 1: 159-67.
Mackay MT, Wiznitzer M, Benedict SL, Lee KJ, deVeber G, Gane- san V, et al. Arterial ischemic stroke risk factors: the Internatio- nal Pediatric Stroke Study. Ann Neurol. 2011; 69(1): 130-40. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22224
Goldenberg NA, Bernard TJ, Fullerton HJ, Gordon A, deVeber G, Geyer R, et al. Antithrombotic treatments, outcomes, and prognostic factors in childhood-onset arterial ischemic stroke: a multicenter, observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2009; 8(12): 1120-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70241-8
Beslow LA, Linds AB, Fox CK, Kossorotoff M, Zuñiga Zambrano YC, Hernández-Chávez M, et al. Pediatric ischemic stroke: an infrequent complication of SARS-CoV-2. Ann Neurol. 2021; 89(4): 657-65. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25991
Ichord RN, Bastian R, Abraham L, Siddiqui A, Askalan R, Benedict S, et al. Interrater reliability of the Pediatric National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (PedNIHSS) in a multicenter study. Stroke. 2011; 42(3): 613-7. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.607192
de Castro de Castro P, Vázquez López M, Gil Núñez A, Chacón Pascual A, Miranda Herrero MC. Tratamientos agudos de reca- nalización en el ictus arterial isquémico pediátrico posnatal. Código ictus pediátrico. An Pediatr (Barc). 2023; 99(1): 44-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anpedi.2023.05.005
Rivkin MJ, Bernard TJ, Dowling MM, Amlie-Lefond C. Guidelines for urgent management of stroke in children. Pediatr Neurol. 2016; 56: 8-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2016.01.016
Beslow LA, Dowling MM, Hassanein SM, Lynch JK, Zafeiriou D, Sun LR, et al. Mortality after pediatric arterial ischemic stroke. Pediatrics. 2018; 141(5): e20174146. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2017-4146
Hollist M, Au K, Morgan L, Shetty PA, Rane R, Hollist A, et al. Pediatric stroke: overview and recent updates. Aging Dis. 2021; 12(4): 1043-57. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2021.0219
Ferriero DM, Fullerton HJ, Bernard TJ, Billinghurst L, Daniels SR, deVeber G, et al. Management of stroke in neonates and children: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association/ American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019; 50(3): e51-96. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000183

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2024 Boletín de Pediatría